The Transboundary Diagnostic Analysis (TDA) and the Strategic Action Program (SAP). The TDA is the analytical component that identifies and analyses the transboundary problems, their impacts and causes. The SAP is the strategic component that focuses on strategic thinking, planning and implementation. Both the TDA and the SAP components should be highly collaborative and fully engage with the key stakeholders from the water system. This menu focuses on the TDA and the steps required to develop the key components of the final document.
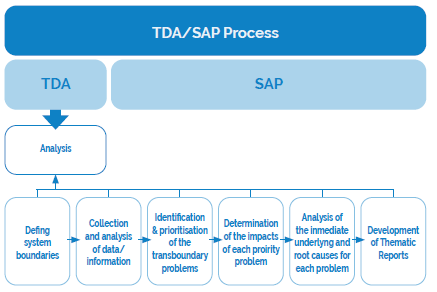 Schematic outline of the TDA process
Schematic outline of the TDA process
The main technical role of a TDA is to identify, quantify, and set priorities for environmental problems that are transboundary in nature. The following indicates the key activities in the TDA process (not necessarily as sequential steps) include:
The TDA provides the factual basis for the strategic component of the TDA/SAP Process – strategic thinking, planning and implementation of the SAP. In addition to this, however, the TDA should be part of a process of engagement and collaboration with stakeholders through the initial TDA steps and the subsequent development of alternative solutions during the formulation of the SAP. Consequently, studies of institutional capacity, governance, and investment are all essential components of the TDA.
